The Raspberry Pi HQ Camera is an innovative, high-quality camera developed by the Raspberry Pi Foundation. In this blog post, we’ll look at the characteristics of the Pi HQ and discuss why it is a solid option for astrophotography.
Key Characteristics of the Pi HQ Camera
High-Resolution Sensor (12.3 MP)
The Pi HQ Camera features the Sony IMX477 sensor, capable of producing 12.3 MP images. This high resolution is crucial for astrophotography, where the fine details of celestial objects are important. This high resolution captures sharp, clear, and detailed images.
Compatible Lenses
The camera supports a variety of C/CS-mount lenses with adaptors to convert to fit 1.25″ eyepiece holders with standard filter threads. There is also an M12 variant available, making the Pi HQ Camera compatible with a large range of wide angle and fish-eye type CCTV lenses, ideal for All-Sky projects.
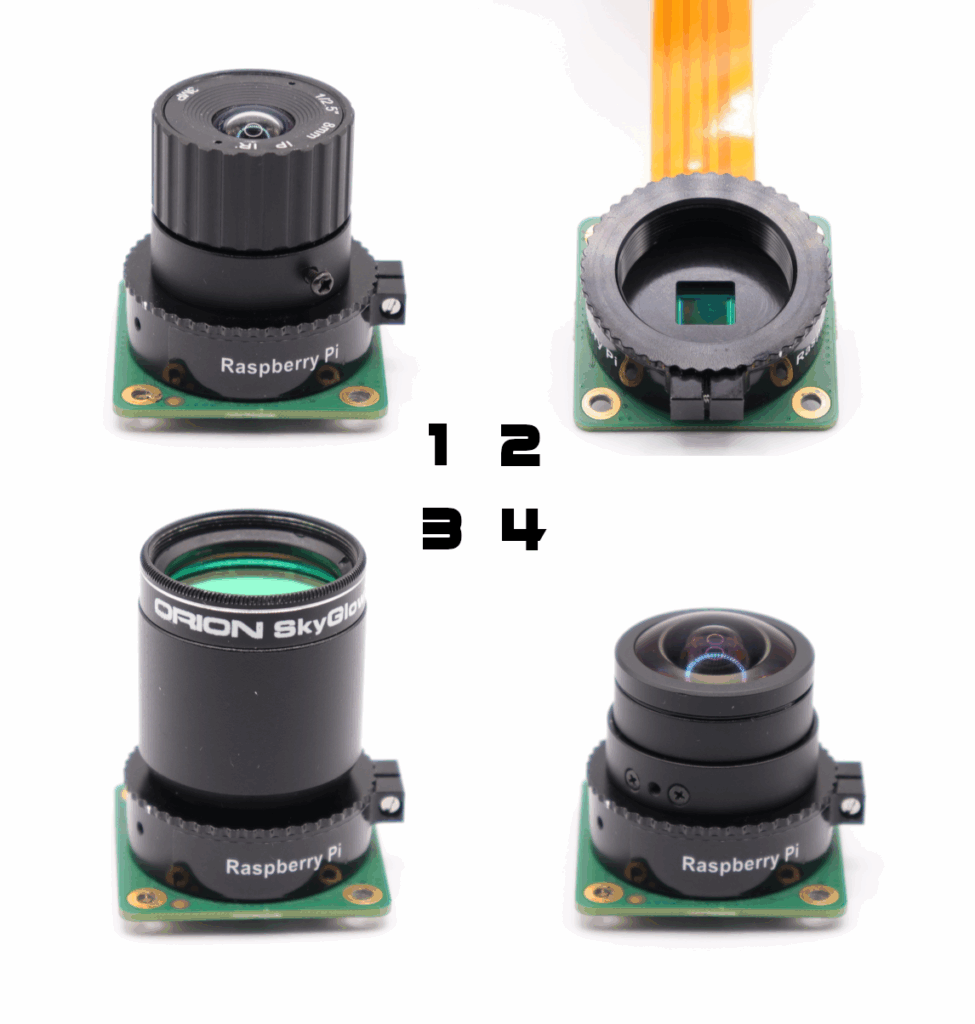

3. 1.25″ adaptor + light pollution filter 4. 180° wide angle All-Sky
Compatibility with Tripods and Telescope Mounts
The Pi HQ Camera has a standard tripod thread (1/4″ – 20 UNC), making it easy to attach to a variety of tripods, telescope mounts, or custom rigs. This allows you to capture stable, long-exposure images without the risk of camera shake, which is essential for clear astrophotography.
Low-Light Performance
The Sony IMX477 sensor in the Pi HQ Camera offers excellent low-light sensitivity, enabling you to capture the faintest of celestial objects.
Affordable Price Point
One of the main advantages of the Pi HQ Camera is its affordability. While traditional astrophotography equipment like dedicated cameras or CCDs can be prohibitively expensive, the Pi HQ Camera is relatively budget-friendly. This makes it an attractive option for beginners and hobbyists who want to explore astrophotography without investing heavily in expensive gear.
Integration with Raspberry Pi
The Pi HQ Camera is specifically designed to work seamlessly with Raspberry Pi computers, known for their versatility and accessibility. The camera is easily controlled through the Raspberry Pi’s Command Line Interface (CLI) using the rpicam-apps library, and with software libraries such as PiCamera2 library for Python, allowing for easy integration and automation.
Datasheet
| Sensor Model | IMX477R stacked, back-illuminated, colour |
| Shutter Type | Rolling shutter |
| IR Sensitivity | Visible light |
| Active Pixels | 4056 × 3040 pixels |
| Lens Mount | C/CS or M12 |
| Still Resolution | 12.3 megapixels |
| Image Sensor Format | CMOS Diagonal 7.857 mm (Type 1/2.3″) |
| Chip Size | 7.564 mm (H) × 5.476 mm (V) |
| Pixel Size | 1.55μm×1.55μm |
| Output | RAW12/10/8, COMP8 |
| Video Modes on Raspberry Pi | 2028 × 1080p50, 2028 × 1520p40 and 1332 × 990p120 |
| Back focus | 12.5mm–22.4mm (C/CS Mount variant) 2.6mm–11.8mm (M12 Mount variant) |
| Tripod Mount | 1/4”-20 |
| IR Filter | Integrated |
| Connection to RPi5 | 15-pin CSI to 22-pin “mini” FPC ribbon cable |
| Size | 38 mm × 38 mm × 18.4 mm (excluding lens) |
| Weight | 30.4g |
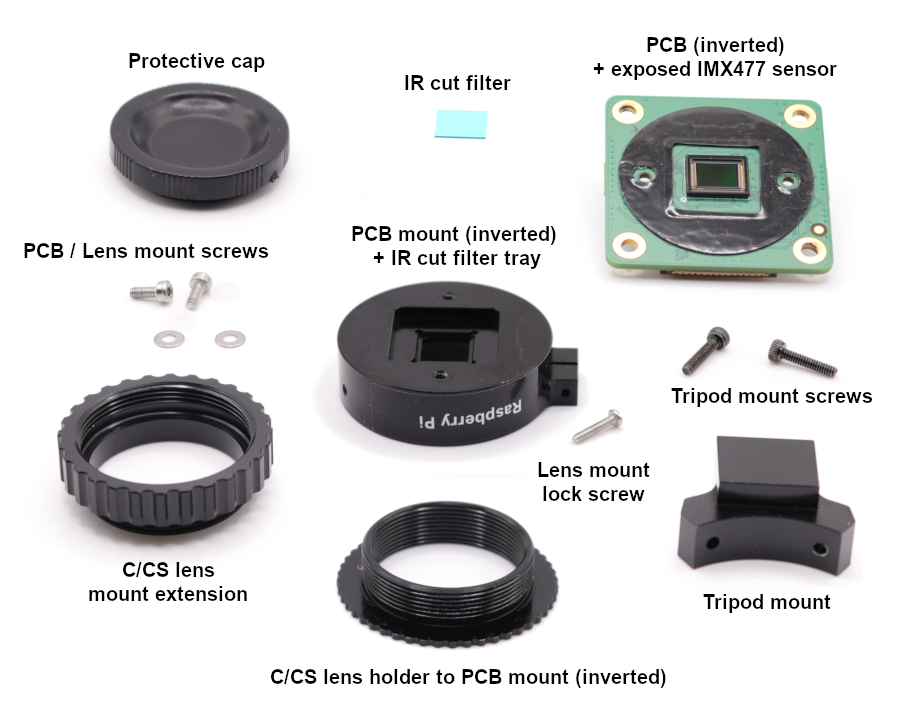
We took one apart, so you don’t have to!

Limitations
| Maximum Exposure Time | 670.74 seconds |
| Minimum FPS | 2 |
| Minimum Exposure Time | 5μs |
| Maximum Exposure Time | 1 / CAM_FPS seconds. E.g. 33ms @ 30FPS |
| Maximum Analogue Gain | 22 |
| Maximum Digital Gain | 4 |
| Maximum Multiplied Gain | 88 ( 22 x 4 ) |
IR-Cut Filter
The Pi HQ camera includes an IR cut filter to ensure accurate colour reproduction in images. This filter blocks infrared (IR) light, which can cause colour distortion and reduced contrast, especially in daylight. Without it, images would appear washed out or have inaccurate colours due to the camera sensor’s ability to detect a wider spectrum of light than the human eye. The filter is a physical component located on the main housing, above the IMX477 CMOS sensor.
While not designed for easy removal, the IR cut filter can be removed quite easily, though doing so may void the warranty and potentially affect image quality.
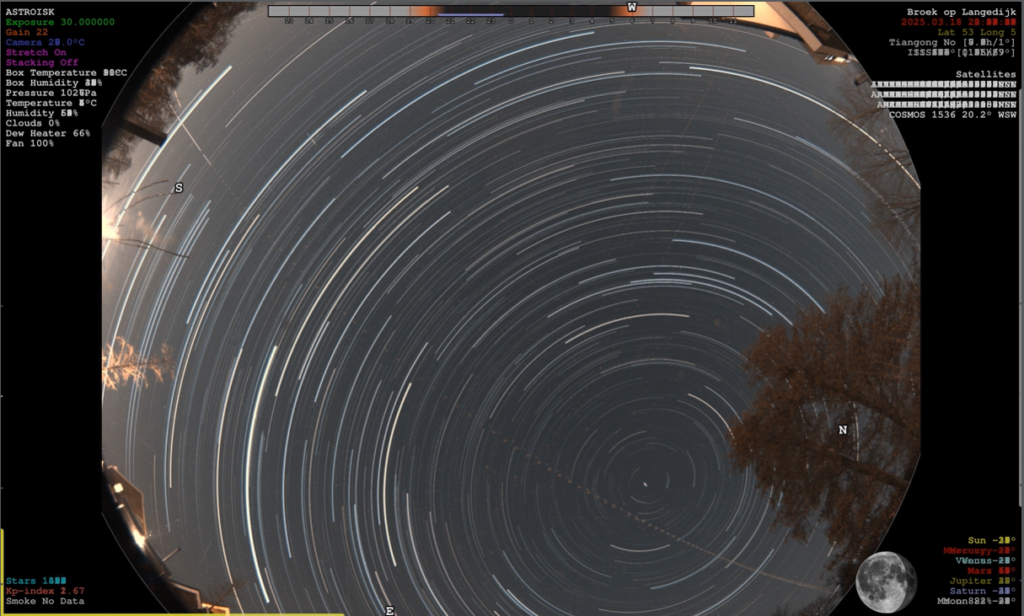
Use in All-Sky Projects
Whether you’re a hobbyist looking to capture meteor showers or a researcher conducting sky surveys, the camera’s combination of high resolution, interchangeable lenses, and compatibility with the Raspberry Pi makes it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications, including the two popular All-Sky solutions which are compatible with the Raspberry Pi 5:
Both solutions provide direct support for the Pi HQ camera, with INDI-AllSky also incorporating a camera simulator, so you can see what your images will look like for a wide range of lenses, before you make any commitment to buy.


Conclusion
The Pi HQ Camera offers an impressive set of features for its price, making it a fantastic option for astrophotography enthusiasts. With its high-resolution sensor, manual control options, and adaptability to different lenses and mounts, it provides the tools necessary to capture stunning images of the cosmos. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to upgrade your astrophotography setup without breaking the bank, the Pi HQ Camera is a compelling choice that strikes a balance between quality and affordability.
Happy stargazing!